In the evolving landscape of data management, businesses are continually seeking ways to harness the full potential of their data. The concept of data mesh has emerged as a significant paradigm, advocating for decentralized data ownership and democratized access to data and analytics. However, implementing data mesh principles can be challenging, especially in diverse technological environments that include traditional data warehouses, modern data lakes, and emerging data lakehouses. Enter data fabric, an architectural framework designed to address these challenges and enhance the implementation of data mesh. In this blog post, we will explore what data fabric is, the problems it solves, and its benefits in modern data architecture.
Understanding Data Fabric
Data fabric is an architectural framework that supports the implementation of data mesh principles. It aims to provide a unified and consistent way to manage, access, and govern data across various environments, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid settings. The primary goal of data fabric is to democratize data and analytics, making it easier for business units to extract value from data while allowing them to choose the technology stacks they are most comfortable with. This includes working with diverse data types from structured data to unstructured data and semi-structured data.
The Role of the Data Platform Team
The data platform team plays a crucial role in implementing the frameworks, philosophy, and concepts of data mesh. They are responsible for ensuring that the organization's data infrastructure supports the decentralized and democratized approach promoted by data mesh. This includes managing connections between traditional data warehouses, scalable data lakes, and modern feature stores for machine learning applications.
Architectural Framework: Data Fabric
One of the key architectural frameworks that has emerged from the data mesh discussion is data fabric. This framework is designed to address several challenges that organizations face when implementing a data mesh, particularly when dealing with streaming data architectures and ensuring data quality through contracts.
Challenges in Implementing Data Mesh

- Data Silos: In many organizations, different departments use their own infrastructure to manage data, leading to the creation of data silos. While this approach works well within individual departments, it hinders collaboration and the creation of cross-departmental data products. For example, marketing might use data lakes for campaign analytics while finance relies on traditional data warehouses for reporting. Data fabric aims to break down these silos by providing a unified layer that allows seamless data access across departments.
- Data Duplication: Creating data products often requires copying data from one infrastructure to another, resulting in multiple copies of the same data. This duplication not only increases storage costs but also complicates data governance and makes it difficult to maintain data quality standards. Data fabric addresses this issue by enabling data virtualization, which allows users to access data without having to move or duplicate it.
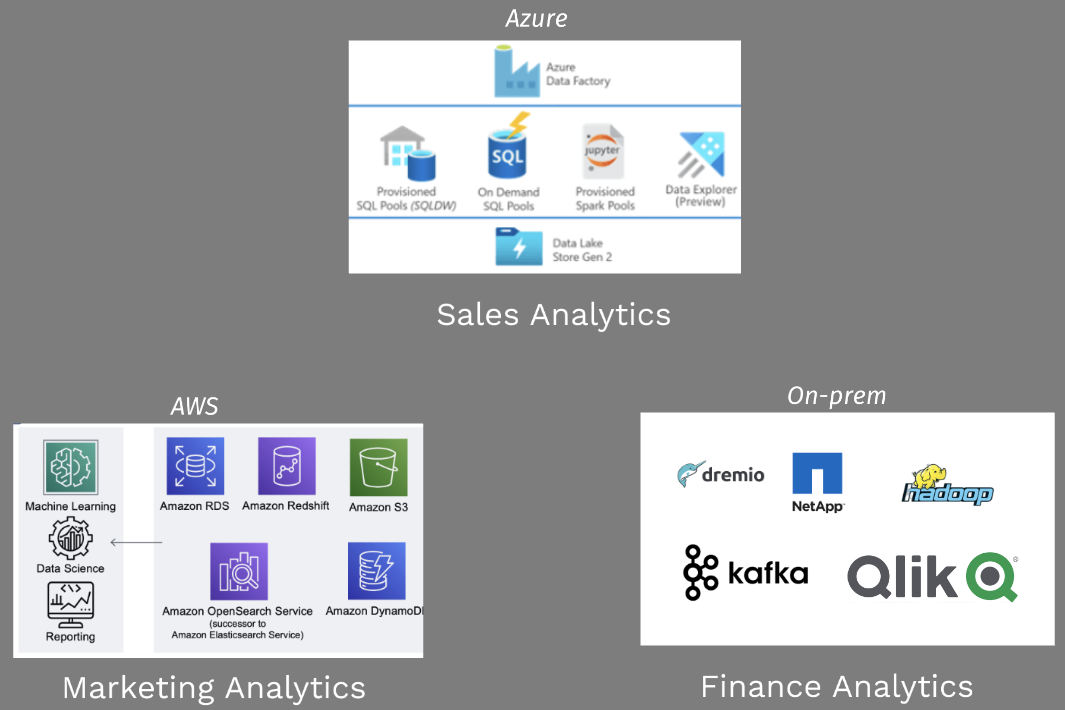
- Diverse Tech Stacks: Organizations often have diverse technology stacks, with different departments using different tools and platforms. For example, marketing analytics might be hosted on AWS with data lakes, while sales could use Azure with data warehouses, and finance might rely on on-premises solutions due to regulatory requirements. This diversity poses several challenges, including data integration, security, and governance. Data fabric provides a standardized approach that overlays existing environments, allowing organizations to manage data more effectively without requiring a complete overhaul of their technology stacks.
- Data Format Variability: Different departments may store data in various formats, from structured data in relational databases to unstructured data like documents and images, requiring additional effort to unify these formats for analysis. Data fabric helps manage and organize data through data cataloging and profiling tools, which standardize data formats and make them easier to analyze.
- User Experience: The use of diverse technologies means that users often have to learn new tools and languages to access different datasets, slowing down analysis and reducing efficiency. Data fabric simplifies user experience by providing a unified semantic query layer, which allows users to query data using familiar interfaces, whether they're accessing vector databases for similarity search or traditional data warehouses for reporting.
- Security and Governance: Different technologies have unique security and governance implementations, making it challenging to unify these controls across the organization. Data fabric addresses this by providing a consistent layer for security and governance, ensuring that data remains secure and compliant across all environments, from feature stores to streaming data platforms.
- Monitoring and Audit Logs: Managing audit logs and monitoring data usage can be complicated due to the need to gather logs from diverse technologies. Data fabric simplifies this process by providing centralized monitoring and logging capabilities, essential for maintaining data contracts and quality assurance.
- Billing and Licensing: A diverse data landscape makes it difficult to visualize and control costs across different platforms, whether it's cloud-based data lakes, on-premises data warehouses, or specialized vector databases. Data fabric helps organizations manage billing and licensing more effectively by providing a unified view of all data-related expenses.
The Benefits of Data Fabric
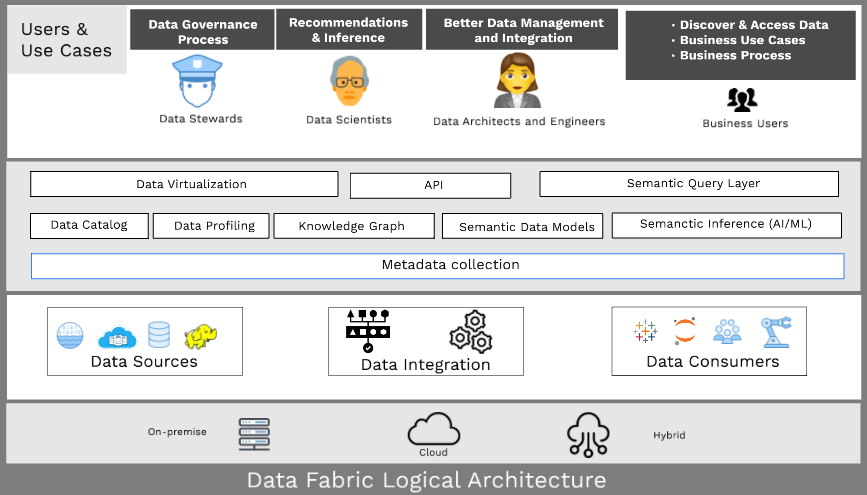
Automated Metadata Collection
The first step in implementing a data fabric architecture is the automated collection of metadata from all data sources, including structured data from databases, semi-structured data from APIs, and unstructured data from documents and media files. Metadata provides critical information about data, such as its source, format, and usage. By collecting and organizing this metadata, data fabric creates a foundation for effective data management across diverse environments.
Building a Semantic Layer
A semantic layer built on top of the metadata allows the creation of business-specific data models. This layer translates complex data structures into understandable business terms, enabling teams to create different models using the same dataset. For instance, sales and marketing teams can develop distinct models tailored to their specific needs, whether they're working with feature stores for machine learning or traditional data warehouses for reporting.
Knowledge Graphs
Data fabric uses knowledge graphs to connect data across datasets, creating a graph of entities and their relationships. Knowledge graphs enhance data discovery and provide a comprehensive view of data relationships, making it easier to analyze and derive insights. This is particularly powerful when combined with vector databases for semantic search and similarity matching across different data types.
Data Catalog and Profiling Tools
Data catalog and profiling tools help manage and organize data within the data fabric framework. These tools provide a centralized repository for data assets, enabling users to easily discover, understand, and access data across different systems, from data lakes to streaming data platforms. This centralized approach supports the implementation of data contracts for quality assurance.
Semantic Inference Layer
Powered by AI and machine learning, the semantic inference layer allows users to query data using natural language. This feature simplifies data interaction, making it accessible to users who may not have technical expertise in SQL or other query languages. The layer can work across different data types and storage systems, from vector databases to traditional data warehouses.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization unifies access to data across different technologies, enabling users to run queries without having to learn new languages or move data between environments. This approach reduces the complexity of data integration and improves efficiency, whether users are accessing structured data from warehouses or unstructured data from lakes.
Simplified Data Queries
The semantic query layer in data fabric provides interfaces similar to ChatGPT, simplifying data queries and making it easier for users to interact with data. This layer abstracts the complexity of underlying data structures, allowing users to focus on deriving insights whether they're working with feature stores for ML applications or real-time streaming data.
Realizing the Potential of Data Fabric
The benefits of data fabric are significant. By providing a unified layer for data governance, access, and integration, data fabric enhances the ability to manage and utilize data across the organization. Business users can more easily discover and access data, improving business processes and decision-making. Data scientists can leverage data across silos to create recommendations and machine learning applications using feature stores and vector databases, driving innovation and value.
Improved Data Governance
Effective data governance is crucial for ensuring data quality, security, and compliance. Data fabric enables consistent governance processes across diverse environments, reducing the effort required to manage data and ensuring that data remains reliable and secure. This includes implementing data contracts across different systems and maintaining quality standards whether data resides in data lakes or data warehouses.
Enhanced Data Discovery
Data fabric improves data discovery by providing centralized tools for managing and cataloging data. This makes it easier for users to find the data they need and understand its context, leading to more informed decision-making. Users can discover everything from structured datasets to vector embeddings through a unified interface.
Streamlined Data Integration
By enabling data virtualization, data fabric simplifies data integration and reduces the need for data duplication. This not only lowers storage costs but also minimizes the complexity of data management, allowing organizations to focus on deriving value from their data across different architectures, from traditional data warehouses to modern data lakehouses.
Empowering Business Users
With data fabric, business users can access and interact with data more easily, improving their ability to drive business outcomes. The use of natural language queries and intuitive interfaces makes data analysis accessible to a broader audience, fostering a data-driven culture. Users can work with diverse data types and systems without needing deep technical knowledge of each platform.
Supporting Data Scientists
Data scientists benefit from the ability to access data across silos, enabling them to create more comprehensive models and analyses. This enhances their ability to develop recommendations and machine learning applications using feature stores, vector databases, and streaming data architectures, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Data fabric represents a transformative approach to data management, addressing the challenges of implementing data mesh and providing a unified framework for data governance, access, and integration. By leveraging automated metadata collection, semantic layers, knowledge graphs, and data virtualization, data fabric enables organizations to harness the full potential of their data across diverse environments. Whether you are a business user, data scientist, or IT professional, understanding and implementing data fabric can significantly enhance your ability to manage and utilize data, driving better business outcomes and fostering a data-driven culture. Consider how data fabric can integrate with your existing infrastructure, from data lakes and data warehouses to vector databases and feature stores, creating a comprehensive and unified data ecosystem.
Learn more about Data Fabrics and other data architectural frameworks in the best selling course on Udemy on this topic.